HR ANALYTICS
How to Use HR Dashboards to Drive Better Business Results
Give your HR teams the power to drive business insights, inform strategies, and make key decisions with a centralized HR dashboard. With data and insights in one place, insights are at their fingertips.
Get a demo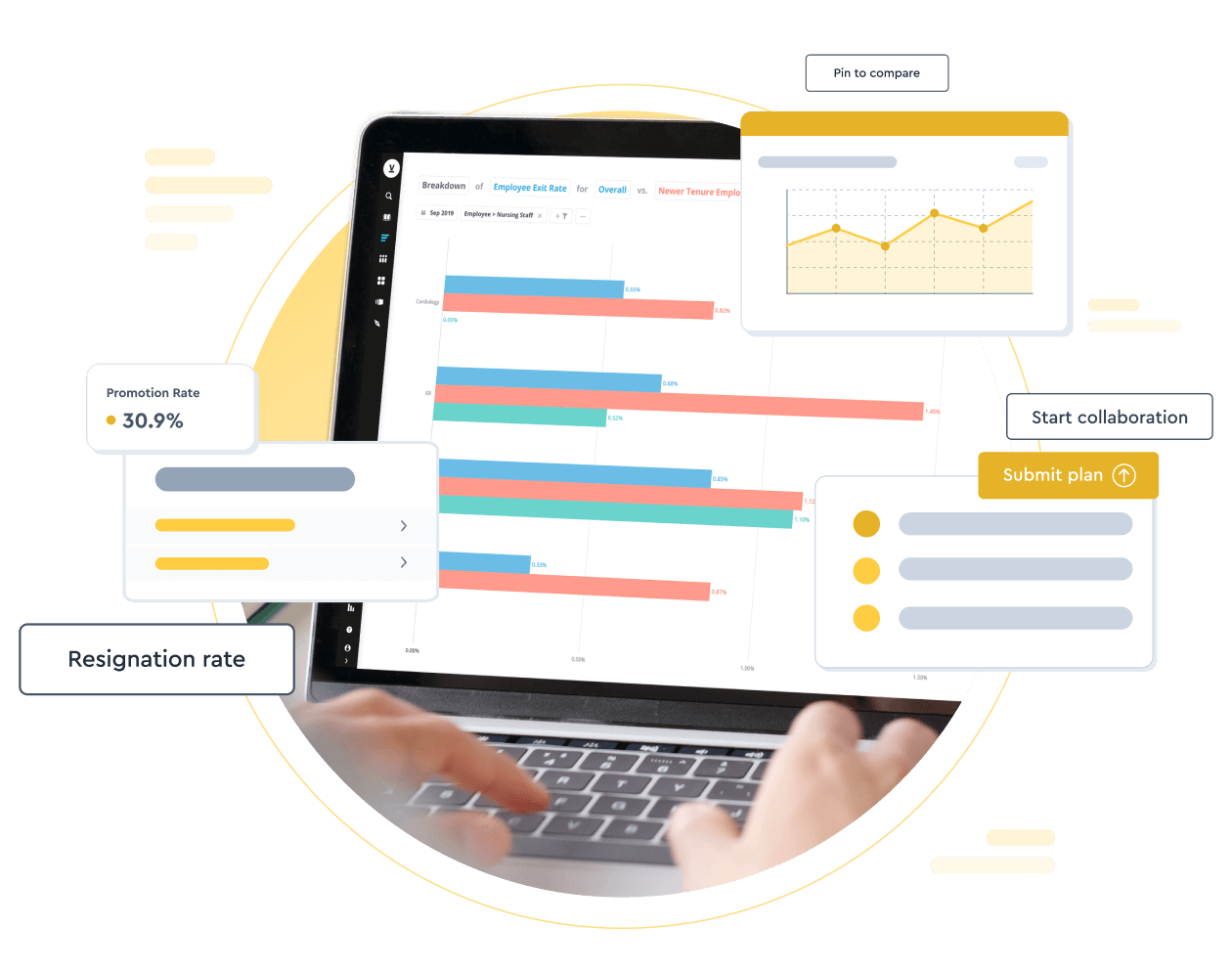
Table of contents
What is an HR dashboard?Pros and cons of HR dashboardsProcess for developing and using HR dashboardsExamples of HR dashboardsTrack metrics that matter in one viewWhat is an HR dashboard?
An HR dashboard is a business intelligence tool that allows businesses and HR teams to record, evaluate and report on various HR performance metrics. The idea of a dashboard, generally, is that of a high-level and interactive summary of multiple types of information, from potentially multiple data sources, that can be easily accessed and analyzed.
Interactive HR dashboards split a single screen into several individual cells or widgets that summarize and present data through numbers, graphs, tables, and various other visuals. These visuals are often accompanied by links that let users drill down into more detail on specific metrics or data sources. This is instead of, for example, a single static report on attribution rates or multiple reports on various HR metrics that are spread across different screens or documents.
HR dashboards might be broad, encompassing all of the information and data needed for the HR function. Or,an HR team may have multiple dashboards specific to various HR roles. This could include a dashboard on employee satisfaction, one on training and development, and another on executive compensation, for instance. The goal in all cases is to aggregate, simplify, and present data in a single screen to make it easier to quickly view, analyze, and take action on specific HR metrics.
HR data is the key to making sound strategic business decisions. Dashboards can help communicate data in an immediate and impactful way.

Pros and cons of HR dashboards
HR dashboards are widely used, and for good reason. They offer a number of benefits for HR teams and companies overall. While there are many pros to their use, though, there are also a few cons or drawbacks.
Let’s explore both.
Pros of HR dashboards
The core benefit of HR dashboard is their ability to simplify and centralized key metrics and data points that HR teams use to drive their strategies and make decisions.
Some specific benefits of HR dashboards include:
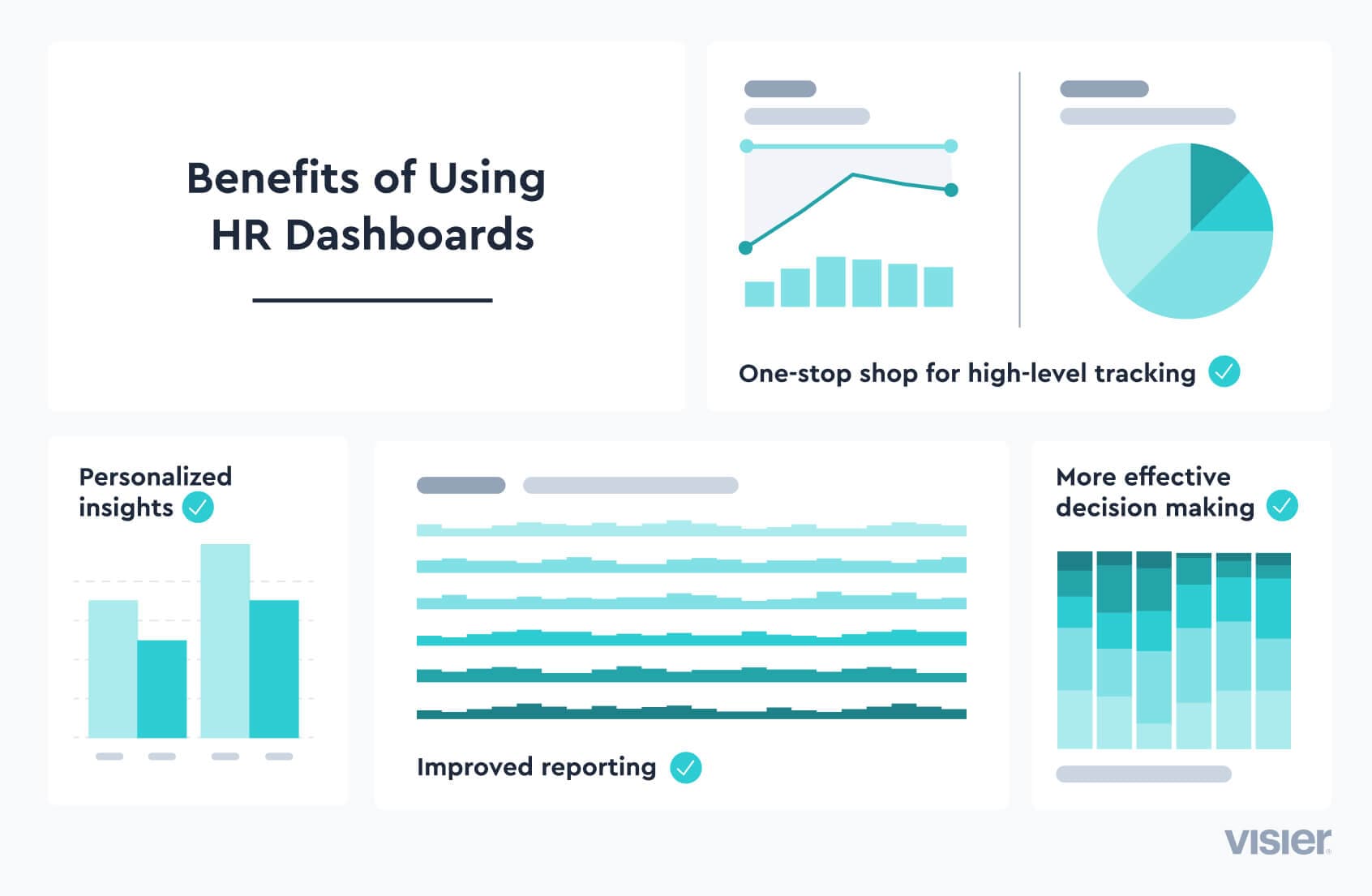
One-stop shop for high-level tracking. Dashboards provide high-level summaries of a wide range of important information, allowing decision makers and those responsible for monitoring, tracking and reporting information an efficient one-stop shop to help them stay informed.
User Interface. It can be exhausting to pour over pages and pages of text and figures in a Word document, spreadsheet, or even a slide show. HR dashboards are typically designed with a user-friendly interface in mind to make it easier to navigate all crucial data quickly and conveniently.
Personalization. Many HR dashboards allow individual users to customize their own personal dashboard to select and organize the cells and their filters to meet their personal data needs. This allows one application to serve a variety of functions for a variety of users. Personalization is especially important in environments where leaders are committed to data democratization (i.e. where data is shared broadly to help both managers and employees track progress).
Reporting. Many HR dashboard solutions allow users to create reports based on the information displayed within the dashboard so other stakeholders can see exactly what the user is seeing. These reports can also be set up with automated distribution in many cases. For example, an HR team might set up their dashboard’s reporting to send a summary of employee satisfaction surveys to relevant managers each quarter.
More effective decision making. In general, HR dashboards make it easier to access information, and easier access to information tends to equate to more effective decision making.
Cons of HR Dashboards
Dashboards tend to be highly personalized and customized, meaning the disadvantages that exist with respect to HR dashboards are often the result of how a particular dashboard is set up and used as opposed to HR dashboards generally. Nevertheless, it’s important to be aware of some key challenges with such tools.
Bias toward historical and current data. Dashboards present information that is currently available. That means data from today (if it’s been gathered and processed already) and data about the past. HR dashboards aren’t necessarily great at providing information about the future; however, it is certainly possible to set up an HR dashboard to display data about a predicted future state. The caveat here is that this future state may never materialize as predicted, making such a dashboard use case inherently prone to inaccuracy.
Lack of prioritization. Dashboards are designed to present a variety of information in a single place. This can create the impression that all of the information on the dashboard is of equal significance, which is rarely the case.
Oversimplification. It’s not practical to use a dashboard to provide highly detailed information. It would simply be too cluttered or too massive. It’s useful to get the big picture of what’s going on, but a dashboard by itself is not a great tool for gathering and reporting detailed insights.
Lack of analysis. HR dashboards, by definition, present data in a siloed and single-dimensional manner. Each widget or cell in a dashboard is designed to present a real-time or historical version of a specific HR metric. While this is useful for obtaining snapshots for those metrics, it doesn’t afford the deep analysis that comes from working with that data in a tool like Excel. It’s important, therefore, for HR teams to routinely perform hands-on data analysis to uncover trends and opportunities that may not be evident in a dashboard.
Process for developing and using HR dashboards
The process for developing and providing HR dashboards to the HR team is fairly simple, but it does involve some key decisions. Most notably, the selection of the right HR dashboard vendor.
Here are the key steps in the overall process.
1. Determine the use case
Setting up an HR dashboard without having an idea of the intended purpose and benefits is a recipe for failure. Some organizations may not even have a great use for such a dashboard at all, although generally just about any organization should be able to make use of an HR dashboard in some manner. Still, it’s critical to understand what an HR dashboard will be used for before doing anything else.
2. Research vendors
Some organizations pride themselves on their home-grown business intelligence tools. However, even sophisticated, multinational software companies go out into the marketplace to find specialized applications rather than building everything themselves.
While there are a variety of HR software vendors, few can offer a full suite of solutions for all of the varied HR functions. Without having this full range of information, though, an HR dashboard can’t provide a complete picture of an organization’s entire HR role.
3. Implementation
Once a vendor has been selected and a purchase agreement signed, the next step is implementing the solution. For an on-premises solution, this would mean installing software on a business’s servers.
For a software-as-a-service (“SaaS”) solution, this would mean the vendor setting up the application on the vendor’s or a third party’s servers.
Installing the software is just part of the implementation process, however. This step also involves building interfaces to data sources, training users on the dashboard, setting up integrations with your existing HR systems, and customizing dashboards to meet specific user needs.
4. Ongoing evaluation and support
Dashboards are typically designed with customization in mind. Users should be encouraged to play around with the selected solution and provide feedback to the organization. That feedback can then be shared with the vendor to address any issues or to request potential enhancements.
Examples of HR dashboards
As noted previously, there are a number of HR dashboards available depending on specific needs.
HR dashboards can help HR professionals and senior leaders answer important questions like:
Is our voluntary turnover rate too high?
How efficient is our talent acquisition process?
Are we seeing higher turnover among women and people of color compared to other employees?
Below are a few examples of the more commonly used HR dashboards.
Executive HR dashboard
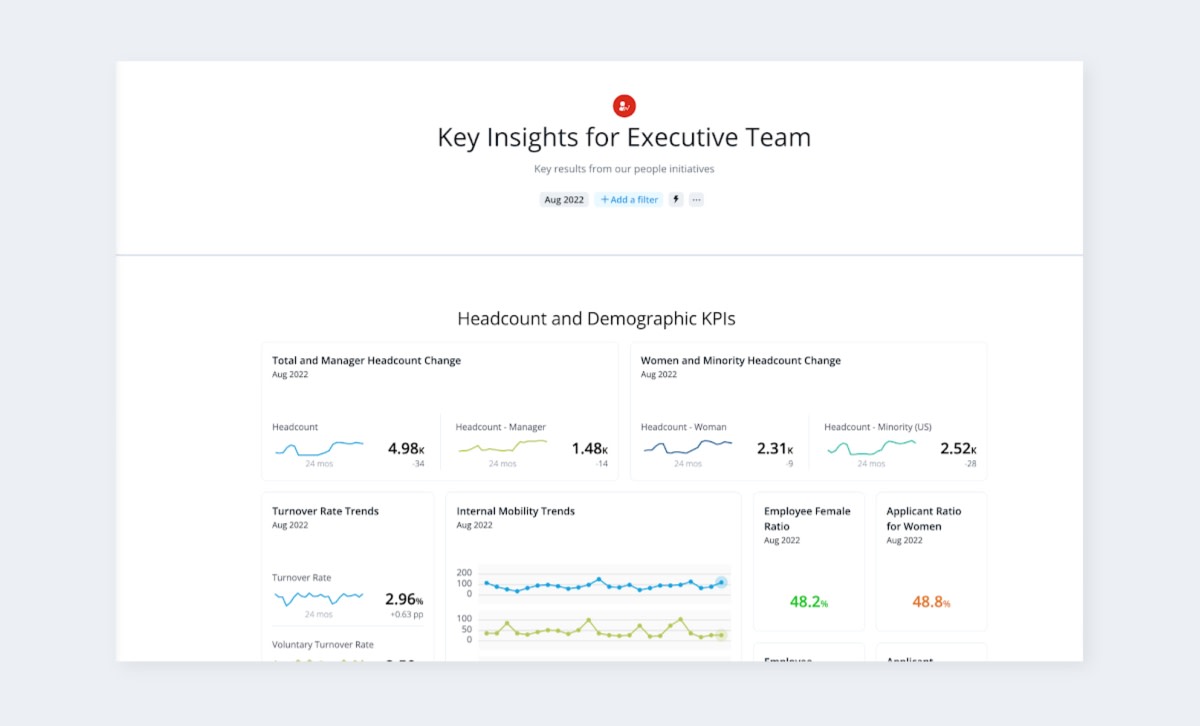
HR executives are busy people. They don’t have the time required to dive down into the weeds on every HR issue. An executive HR dashboard lets HR leaders quickly review the most important information.
Diversity dashboard
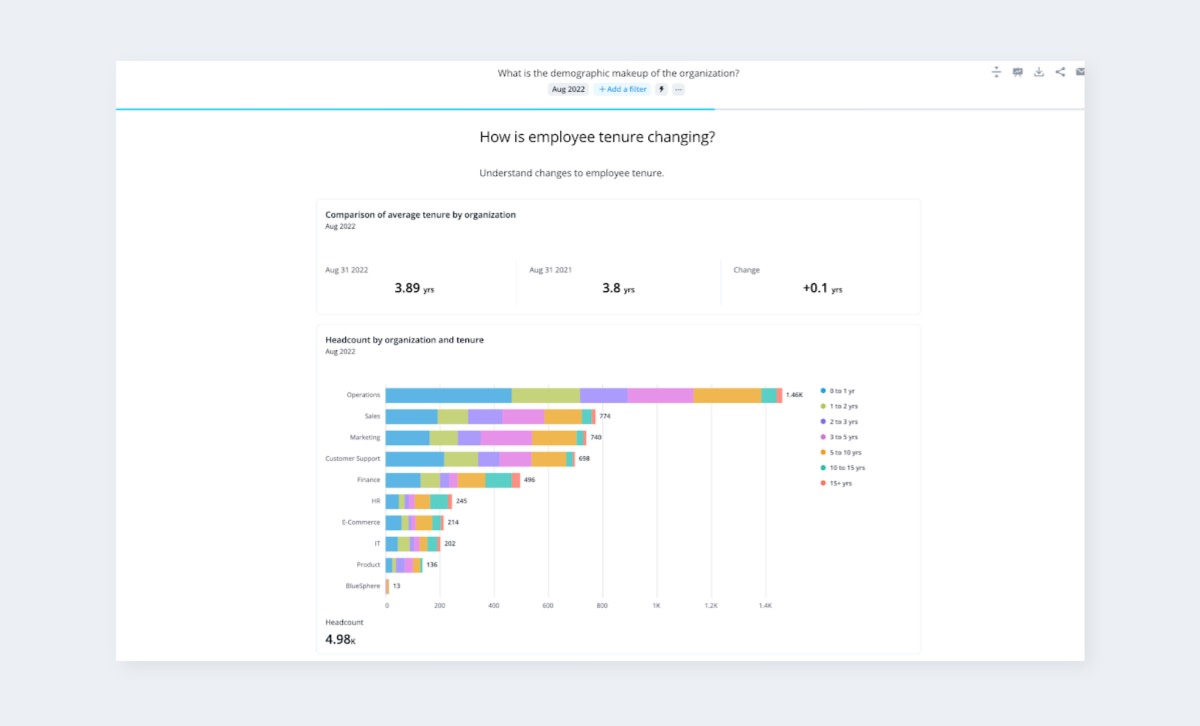
A diversity dashboard focuses specifically on the diversity element of the HR function but still provides a high-level view without getting into minute details. These dashboards might show a summary of employee ethnicity in one cell, gender diversity in another, and diversity metrics specific to certain groups (i.e., executives) in yet another cell.
Recruitment dashboard

HR A recruitment dashboard can look at metrics specific to the recruitment process, such as the length of time a job opening goes unfilled, the number of job requisitions across various departments and the effectiveness of various recruitment marketing outlets.
HR, of course, is a broad function. Because it is, there are a number of other dashboards that HR leaders might choose to implement and monitor. It all depends on the current HR strategy, goals, and objectives. Dashboards should be established to provide critical analytics related to each HR strategy or initiative.
Track metrics that matter in one view
HR dashboards are popular in many organizations because they allow leaders and HR team members to quickly review high-level data relevant to the HR function. Dashboards also provide the ability to drill down deeper through links contained within the dashboard that direct to other solutions or pages. HR dashboards may also provide reporting functionality and allow for customization and intuitive user interfaces.
HR dashboards help you compile all the data you need to see in a meaningful way, quickly and easily. With HR dashboards, you can keep an eye on employee satisfaction and employee engagement to make proactive decisions when problems arise, and evaluate the likelihood of employee turnover and its underlying causes. Use HR dashboards to look at internal staff movement more holistically by illustrating the number of new hires, exits, and internal transfers all in one central location.
Create a strategic compensation dashboard to easily look at comparisons and analyses of employee compensation across job functions, geographic regions, seniority levels, demographics, and employee performance. This can be extremely helpful when trying to get ahead of issues related to pay inequities, or when gathering data for ESG purposes.

![Why HR Dashboards Are Just the Start [IMAGE ASSET]](https://images.ctfassets.net/lbgy40h4xfb7/3T4UoVThzDaryLyZYcvRZP/4a128f8a185148e47034b04e0a71a4f3/pa-dashboard-blog.jpeg?w=1200&h=700&fl=progressive&q=100&fm=jpg)
![Sharing People Data Outside HR to Drive Business Value [CARD ASSET]](https://images.ctfassets.net/lbgy40h4xfb7/32bE6hBJDtBL1iGA94ehpt/508fe3cd9b1fdaf01fa50a0217c8aefd/HBR-report-resource-card.jpg?w=1200&h=627&fl=progressive&q=100&fm=jpg)
![Beyond HR: Democratizing People Data is Key to Business Success [IMAGE ASSET]](https://images.ctfassets.net/lbgy40h4xfb7/2dKTPhdlJqZHbI0vMFCxpg/a5cad5d9ceff2a2abad5877cce12903b/democratizing-people-data-blog.jpeg?w=1200&h=700&fl=progressive&q=100&fm=jpg)