HR METRICS
What is Employee Satisfaction?
Strong employee satisfaction creates positive ripple effects across an organization, including better retention and performance. Learn more.
Explore talent retention
Table of contents
What is employee satisfaction?What are the benefits, pros, and cons of employee satisfaction?What are the process steps in managing employee satisfaction?Examples of employee satisfaction in practiceUse people analytics to impact employee satisfactionWhat is employee satisfaction?
Most of us accepted long ago that we work to pay the bills and feed our families and that we shouldn’t expect to love logging on or showing up to work every day. Still, some jobs are more enjoyable than others based on workplace culture, flexibility, personal relationships with coworkers, compensation, company values and mission, and a variety of other factors that all contribute to what is generally referred to as “employee satisfaction.”
Gallup research indicates that what has been called the “great resignation” is really the “great discontent.” They report that 48% of the working population in the US is actively seeking another job. There are a variety of reasons for this including: lack of flexibility, burnout, disconnect to company culture, not seeing a clear career path, or not feeling that their time is spent on meaningful work.
This potential for turnover is obviously a concern for companies of all kinds, as is the potential for disengagement and low productivity among employees who choose to stay. These employees have come to be referred to as “quiet quitters.”
Consequently, companies spend a lot of time, effort, and resources trying to measure and improve employee satisfaction with mixed results. In this article, we’ll define employee satisfaction, discuss some pros and cons of employee satisfaction, outline the general process for improving employee satisfaction, provide some examples and, finally, discuss how Visier’s suite of management solutions can help boost employee engagement for businesses of all types.
What is employee satisfaction
Employee satisfaction is a general term that’s used to describe how satisfied or content employees are with their jobs and company. It’s a measure of how content workers are with various elements of their jobs, employee experience, daily work, management, and compensation.
Indeed, employee satisfaction can be hard to define and quantify because it often means different things to different people and depends to a large degree on the subjective importance individual employees place on different aspects of their jobs.
For example, a job may pay $500,000 per year but require an employee to work 80+ hours per week and be available 24/7 to deal with difficult clients and demanding superiors. Some workers might find that job very satisfying based on the compensation alone. For others, the significant and demanding workload might be a nightmare.
Measuring employee satisfaction
Often, the best way to measure employee satisfaction is simply to ask employees how satisfied they are with their jobs. Many, many companies routinely conduct surveys asking that exact question, among others, to get a general sense of company-wide employee satisfaction..
Additionally, discussions between employees and their supervisors can help dig deeper into the individual elements of employee satisfaction, including things like workplace relationships, compensation, workload, and other factors.
In short, employee satisfaction is a subjective measure of how content an employee is with their job and employer. As we’ll discuss in the process section below, there are many ways to more specifically define the various elements of employee satisfaction.

What are the benefits, pros, and cons of employee satisfaction?
Employee satisfaction can mean different things to different people, so the benefits and drawbacks depend to an extent on which specific aspect is being considered.
The following pros and cons are intended to be general enough to cover most interpretations of employee satisfaction.
Pros
One of the biggest benefits of employee satisfaction is how it supports an organization’s staffing needs. Happy employees are less likely to be subject to trends like “quiet quitting” or “the great resignation.” Attracting and retaining employees is obviously top of mind for all employers today. Employee satisfaction is a primary area of focus for that reason.
Satisfied employees also tend to be more engaged in their work and more productive than unhappy employees. That makes sense because everyone tends to put more heart and soul into work that satisfies them. Happy employees are more likely to go the extra mile even when they aren’t required to and are more likely to support the company’s mission and vision.
Satisfied employees also make for a more pleasant work environment, whether that environment is in-person or virtual. They are less likely to engage in negative, passive aggressive, abusive, or harassing behaviors.
Lastly, satisfied employees are also in a position to serve as power brand ambassadors for organizations, from both an employee and customer standpoint. They are more likely to recommend the company as a great place to work and as a great brand, and are more likely to share that sentiment publicly through channels like Glassdoor.
Cons
It may seem counterintuitive to suggest that there can be any negative impacts of satisfied employees, but there are a few to consider.
One potential con of employee satisfaction is that satisfaction can lead to complacency. Humans crave comfort, and employees accustomed to their jobs may have a tendency to simply perform that job as they always have, failing to stretch themselves through additional challenges. They may be reluctant to leave their comfort zone to participate in uncertain new ventures or challenging assignments that don’t seem as pleasant as their current workload.
Another potential drawback of employee satisfaction is that companies that place a great deal of importance on employee satisfaction may develop implicit biases in favor of some personality types and against others. For example, bubbly, outgoing employees may be unconsciously favored by management for doing a better job of outwardly expressing their satisfaction than more reserved staff
who may be just as satisfied, committed, and engaged with their work, but don’t demonstrate that satisfaction through their personalities.
Placing too much emphasis on employee satisfaction may backfire for some companies. For example, a company overly focused on satisfaction may have a chilling effect on employees who have legitimate complaints with aspects of their work or the organization. Because the company is so desperate to increase employee satisfaction, some workers may fear derailing that goal by bringing up issues of concern.
All of these cons can be avoided with sound people management strategies. However, it’s important to be aware of these risks and to proactively take steps to avoid them.
What are the process steps in managing employee satisfaction?
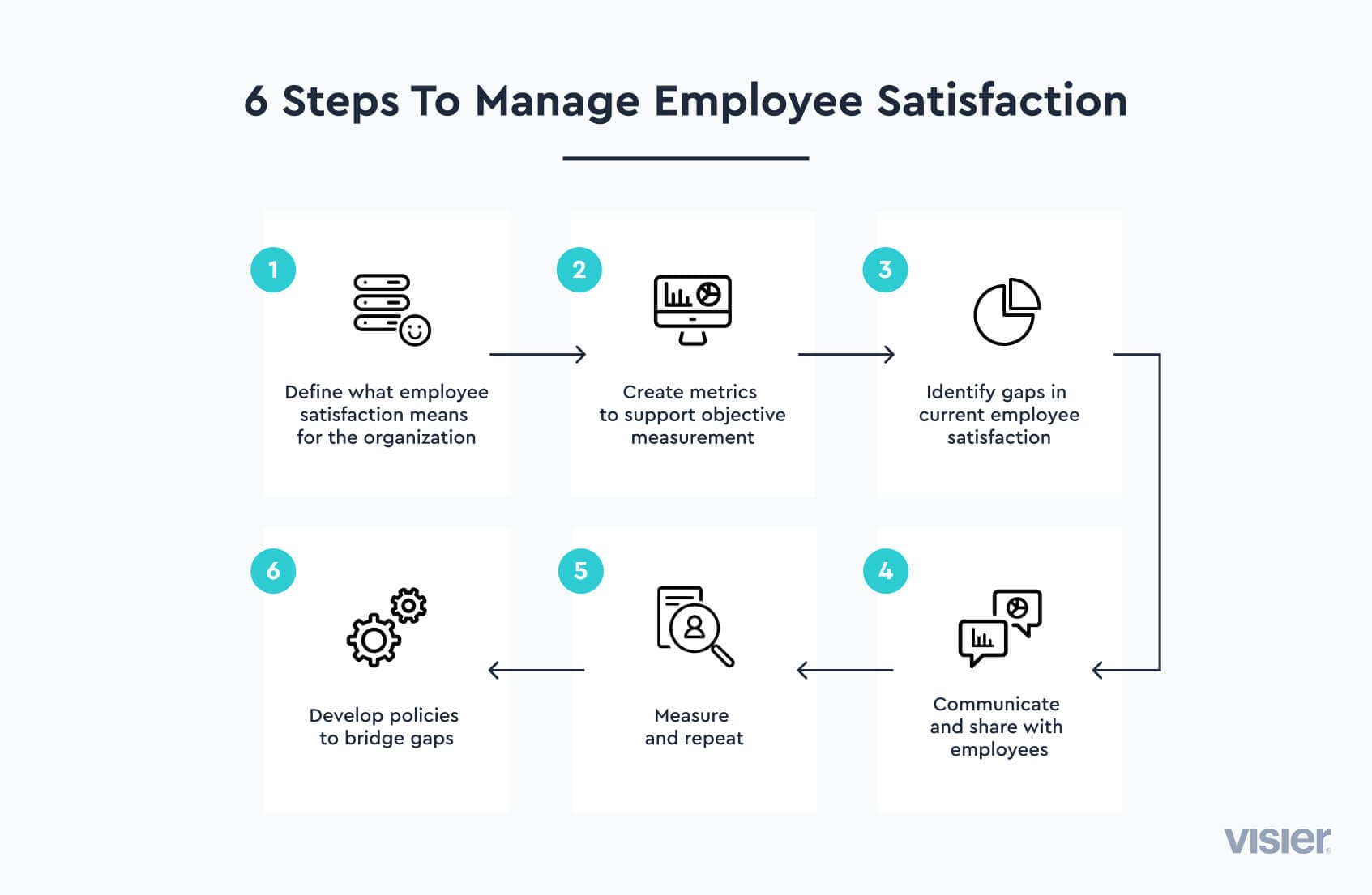
While there are some potential drawbacks to employee satisfaction, it’s hard to argue that satisfied and engaged employees are not a boon to organizations in the vast majority of cases. But how does a company increase and maintain its employee satisfaction? The process below is general enough to work for virtually any organization and provides a step-by-step framework that managers and HR teams can follow.
1. Define what employee satisfaction means for the organization
As noted previously, employee satisfaction means different things to different people (and companies).
Similarly, the different ways in which employee satisfaction manifests itself may be more or less important to different organizations.
Employers need to think about what employee satisfaction means to their individual organization and their team. They also need to think about ways to benchmark that satisfaction and measure it over time. That could be through things like engagement and lower turnover or something less concrete like positive responses on employee surveys. Keep in mind that satisfaction determinants may vary between roles and departments.
2. Create metrics to support objective measurement
Quantifying employee satisfaction through relevant metrics can help companies both establish baselines that can be compared across the organization, and provide a starting point for making measurable improvements. Any process for business improvement needs to have measurable results. There are a variety of metrics companies can use to track employee satisfaction.
One way is simply to ask employees how satisfied they are through a combination of surveys and more in-depth individual or group discussions. These qualitative answers can be analyzed and bucketed into similar themes that demonstrate which factors are most important to employees. Subsequent surveys can then be used to gather ongoing feedback to compare against the original results.
Other methods involve using organizational proxies for employee satisfaction, such as productivity and turnover. While increased productivity and decreased turnover aren’t perfectly synonymous with employee satisfaction, they are key byproducts of a happy workplace.
3. Identify gaps or shortcomings in current employee satisfaction
Most companies would like to do better than they currently are at employee satisfaction, and it’s entirely normal to identify gaps between the current state of affairs and the desired outcome. Once an organization has defined the appropriate metrics tied to its employee satisfaction it can take stock of where it stands today on those metrics, and prioritize areas of opportunity for proactive action.
For example, one gap that exists in many companies today is the failure to provide adequate reskilling and development opportunities for employees. LinkedIn’s 2022 Workplace Learning Report identifies these factors as a top consideration for employees on whether to accept a job, or stay on the job.
4. Develop processes and policies to bridge those gaps and address shortcomings
Obviously, identifying shortcomings should lead to fixing those shortcomings and bridging existing gaps. This might mean rethinking compensation, relaxing strict workplace policies, addressing lingering workplace conflict, introducing new policies or support programs, or taking other actions designed to close identified gaps in current and desired levels of satisfaction.
5. Measure and repeat
Employee satisfaction is not static. It changes over time based on both internal and external environmental impacts. Changing role demands, management personnel and practices, customer expectations and other variables mean that employee satisfaction is a moving target. Because of that, it’s important to measure satisfaction continually to identify new areas of opportunity for improvement and adjusting metrics as appropriate.
For instance, if learning and development is identified as a gap, companies need to put metrics in place to help measure the business impact.
Using the metrics developed in Step 2, companies should be well-equipped to adjust their processes and policies in order to smooth out any wrinkles and strive for continuous, iterative improvement.
6. Communicate
A not uncommon mistake that organizations make when gathering feedback from employees is failing to share that feedback with them, along with information about how existing gaps will be addressed. Communication should be ongoing at all levels of the organization as feedback is gathered and changes are made in an effort to improve employee satisfaction.

Examples of employee satisfaction in practice
So, what does employee satisfaction look like in practice? Here are a few examples of how employee satisfaction manifests as positive behaviors and outcomes for the organization.
An employee notices an open position in her department and forwards the job posting to a highly qualified friend looking for a new job. The employee raves to her friend about what a great place the company is to work.
An employee voluntarily works late to put in extra effort in order to do a great job on a project. Even though he has already done enough to complete the basic requirements of the work, he enjoys the work so much and believes so strongly in the company’s mission that he wants to do a great job to ensure success for his team and for the organization.
An organization has many employees who have been with the company for decades. Employees have options when it comes to where they want to work, and often the biggest salary increases workers gain in their careers come from job switching. Long-term employee retention is a great sign of satisfied employees.
These are subjective indicators of satisfaction, but savvy companies also use data to help them quantitatively measure and impact employee satisfaction.
Panasonic, for instance, used data to link job satisfaction with turnover, demonstrating the importance of focusing on and improving satisfaction. They were also able to demonstrate that productivity increased as work-life integration improved.
Use people analytics to impact employee satisfaction
People analytics is a useful tool to quantify and improve employee satisfaction, and identify employee engagement problems that could drag down performance. When people managers and business leaders have access to HR metrics and HR dashboards, they can proactively track employee satisfaction indicators and address any problems.
Compensation isn’t everything, but it’s one of the things that impacts employee satisfaction. People analytics solutions make it easy to look at comparisons and analyses of employee compensation across job functions, geographic regions, seniority levels, demographics, and employee performance. This gives organizations greater transparency into how its compensation compares to competitors and how it impacts employee satisfaction.
Retention and internal mobility
One way to monitor employee satisfaction is to evaluate the likelihood of employee turnover and the causes underlying turnover. As turnover is a sure sign of poor employee satisfaction, these underlying causes of attrition are generally risk factors for employee dissatisfaction as well.
For many workers, the ability to grow professionally and advance their careers is central to their job satisfaction. Managers can make an impact on employee satisfaction of their teams by mapping out career development plans with key staff.

![6 Signs Your Employee Is About to Resign [CARD ASSET]](https://images.ctfassets.net/lbgy40h4xfb7/1sL4A7XWgw4MFTd4jiZSBs/1d73bd3332da4d34f80fcd87f724b521/resignation-red-flags-resource-card.jpg?w=1200&h=700&fl=progressive&q=100&fm=jpg)
![10 Employee Retention Strategies for Keeping Your Best Talent [CARD ASSET]](https://images.ctfassets.net/lbgy40h4xfb7/5fTeS4wYN3JxW8Z1EqITOY/58937af7349174e26a945aa2878b92c2/employee-retention-strategies-blog.jpg?w=1200&h=700&fl=progressive&q=100&fm=jpg)
